Osteochondrosis is one of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system, well studied, but difficult. This is not just back pain and a lot of discomfort: over time and if left untreated, osteochondrosis can lead to the development of serious disability and significantly reduce the patient’s standard of living. Therefore, it is very serious to take this disease that does not seem to be afraid even at the first signs.
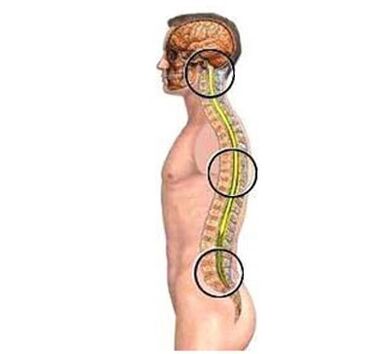
Symptoms
Osteochondrosis is very often undiagnosed for a long period of time. Osteochondrosis syndrome does not even directly point to the spine, disguised as another disease. And the patient "suppressed" the pain syndrome with painkillers, blaming everything on the migraine - at best, and at worst - he was treated for a completely different illness, without seeing an improvement over the years.
In the early stages of the development of the disease, osteochondrosis manifests itself only with minor pain and discomfort after performing intense physical activity or prolonged sitting in an uncomfortable position at a table. The disease progressed over the years, gradually all the symptoms worsened. Characteristic features of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region include:
- numbness and tingling in the limbs. Especially after a long stay in one position or sleep. This is one of the first signs of a spinal problem. After rubbing, the numbness and discomfort quickly passed and did not cause severe discomfort;
- cold sensation, goose bumps on the skin in the hand area, often - on individual hands or fingers, more rarely - in the affected back area;
- painful sensations often have "wrong" localization. Pain can occur both in the affected area of the spine, and radiating (giving) to the chest area, resembling pain in heart disease, can occur during breathing. Therefore, when diagnosing osteochondrosis in the presence of pain in the heart area, ECG will be a mandatory study - to exclude ischemic disease. Also, pain is often given in the scapular area (intercostal neuralgia) or left hand;
- painful sensations often increase at night;
- also patients are often tormented by migraine -like headaches. They can occur on one side of the head and cover the entire head;
- decreased well -being, mood;
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is rarely accompanied by spinal cord compression. But if this happens, the symptoms will be more pronounced: the sensation of pain becomes strong, accompanied by serious disturbances in the work of internal organs.
All symptoms of osteochondrosis are the result of compression of nerve roots that pass through the spinal space. Depending on the area and degree of compression, the symptoms can vary greatly, therefore, at the first suspicion of osteochondrosis, it is very important to make an instrumental study and make a correct diagnosis.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region rarely occurs on its own - the thoracic region is inactive and less stressed, often the disease is combined with cervical osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis treatment methods
Like all degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system, osteochondrosis is treated very difficult and for a long time - there is no easy and quick cure. You have to be prepared for this. It is impossible to reverse degenerative changes in the intervertebral disc. The ideal option is to stop the progression of the disease at an early stage, when osteochondrosis does not impose restrictions on the patient’s lifestyle. In the early stages, it is enough to slightly adjust the patient's lifestyle: to increase physical activity, to create a complete diet. But rarely make a diagnosis at the beginning of the development of pathological changes.
The complex of traditional therapies for osteochondrosis includes:
- Drug therapy. . . It consists of several components:
- with severe pain syndrome, patients are given painkillers. Often these are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Rarely used are steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opiates and opioids. They are more powerful, but have many limitations in their use;
- a mandatory part of treatment is to take supplements and vitamins that strengthen the skeletal system;
- muscle relaxation helps relieve muscle tension. But it should be said that without constant exercise in medical gymnastics, the intake of muscle relaxers is strictly contraindicated;
- taking chondoprotectors helps speed up the recovery process in the affected area, although expert attitudes towards such medications are very vague.
- Drug -free treatmentfar more important for the success of osteochondrosis treatment.
- first of all, one should focus on the implementation of a systematic and correct system of rehabilitation gymnastics. Exercise therapy aims to strengthen the muscular corset around the spinal space, speed up local blood circulation and, with regular exercise, can significantly improve the patient’s condition;
- Physiotherapy treatment helps relieve muscle pain and tension. They act in the same way as anti-inflammatory painkillers, but have fewer contraindications;
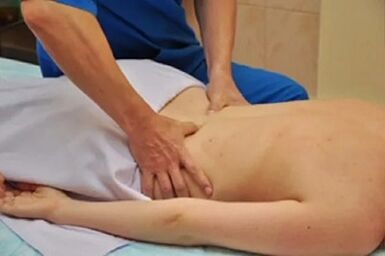
- massotherapy. Both traditional massage therapy and many alternative methods are practiced, the main selection criteria being the professionalism of the specialist and consultation with the attending physician;
- manual therapy;
- traction (traction therapy) on a special simulator. The gentle traction of the spine allows you to relieve muscle tension and reduce symptoms caused by nerve root compression;
- you should also change your approach to your diet, making it more balanced.
Therapeutic training for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
You can do medical gymnastics in special rooms in the hospital and at home. The more frequent and frequent the session, the higher its effectiveness. Organized to hold classes several times a day, the mandatory part of the complex is morning exercises. Each exercise should last from 5 (in the first stage) to 40 minutes, the number of repetitions of each exercise should be from 5 to 20. Here is an approximate set of exercises:
- Lying on your back, the surface should be flat and firm, for convenience, you can put a gym mat. Bend the knees, then simultaneously bend the knees towards the nose and head to the knees. Hold at the top point for a few seconds, return to the starting point, change your legs;
- Universal training - common to everyone from childhood "cats". Get all four with your head down. As you inhale, bend your back as much as possible and lift your head. Then, as you exhale, complete the buttocks and lower the head;
- In the middle of the work day, you can take a short break to do a simple exercise: lift each shoulder as high as possible, while one shoulder goes up, the other goes down;
- Sitting on a chair with your back reaching your shoulder blades (a regular office chair will do), press your back firmly into the back of the chair. Then lift your arms and bend your upper back as much as possible;
- Perform as few circular movements as possible with your arms outstretched. Performed while sitting in a straight hard chair or standing;
- Stand upright with feet shoulder width apart. Hold your hands behind your back under the shoulder blades. Bend as much as possible in the thoracic area, restraining yourself with the hands;
- Also, from a standing position, bent as much as possible, chin inclined to the chest, shoulders to each other. Hold at the lowest position for a few seconds. Then make a back movement: straighten your shoulders as much as possible, bring your shoulder blades together and throw your head back. Exercises are performed at a slow and smooth pace.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region can develop very slowly, without causing much concern for a long time, but as a result, the patient faces many restrictions on his normal lifestyle and the fact that his standard of living continues to decline. Therefore, if you experience the first sensation of discomfort and mild pain, you should see a doctor.






















